Hi everyone, I’m Dr. Satish Verma, and today we’re diving into the world of blood sugar! It’s a fundamental aspect of health, and understanding it empowers you to take charge of your well-being.
Demystifying Blood Sugar
Blood sugar or blood glucose is a circulating blood component that is crucial for energising all the body’s cells. It has its source in the food that you eat, especially in carbohydrates. Blood sugar is a type of sugar that is found in the blood; insulin, a hormone, regulates this blood sugar by opening certain doors and permitting this glucose to enter your cells.
The Importance of Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Knowing your target blood sugar range is critical for maintaining good health. Here’s a breakdown of what’s considered normal:
- Fasting Blood Sugar: This refers to your blood sugar level before eating anything, ideally after an 8-hour overnight fast. A healthy fasting blood sugar level falls between 72 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
- Post-meal Blood Sugar: This measurement reflects your blood sugar level two hours after eating. Ideally, it should be below 140 mg/dL.
Warning Signs of High Blood Sugar
Chronically elevated blood sugar, a hallmark of diabetes, can manifest through various symptoms. If you experience any of these, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: The body attempts to eliminate excess sugar through urine, leading to frequent urination and increased thirst to replenish fluids.
- Fatigue: Cells starved of sugar due to insulin resistance experience a lack of energy, resulting in fatigue.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can affect the lenses in your eyes, causing blurred vision.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: Elevated blood sugar can impair blood circulation and the immune system’s ability to fight infection, leading to delayed wound healing.
Navigating Diabetes Diagnosis
If you suspect you might have diabetes, a doctor can confirm the diagnosis through various tests:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: As mentioned earlier, this test measures your blood sugar level after not eating overnight.
- Haemoglobin A1c (A1c) Test: This test provides a broader picture of your blood sugar control over the past 2-3 months. It measures the percentage of haemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells) that has bonded with sugar.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This test involves drinking a sugary solution and measuring your blood sugar levels at specific intervals afterwards to assess your body’s ability to process sugar.
Taking Control: Monitoring Blood Sugar
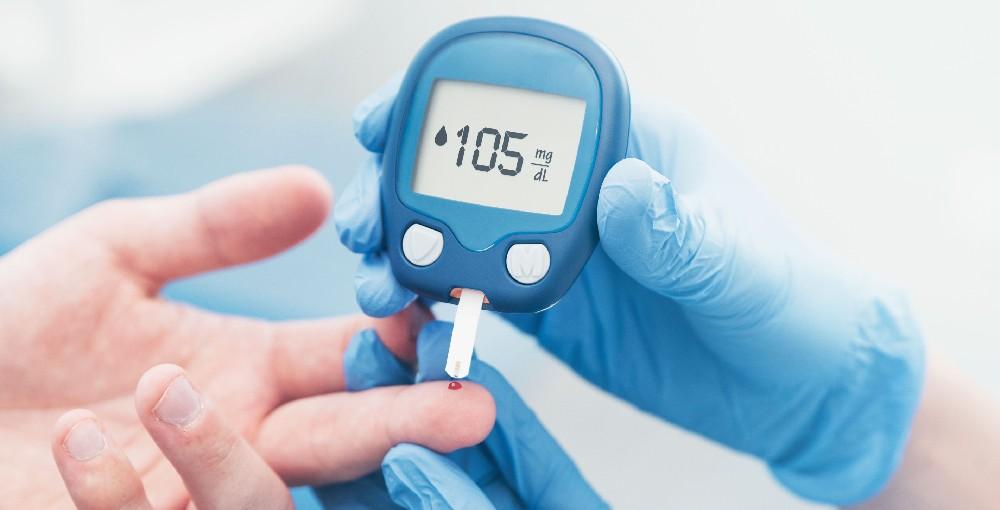
In situations where someone has been diagnosed of having diabetes, it is important for them to begin monitoring blood sugar level. This refers to a glucometer, a hand-held device, which needs a small incision on the finger to get blood samples out of it. The glucometer pricks the efficiency of blood sugar and then gives the details of the same.
Beyond Diagnosis: Embracing Blood Sugar Control
Although being diagnosed with diabetes is certainly a challenge, it’s helpful to keep in mind that you have a community of support. Fortunately there are plenty of good ways to get your blood sugar levels in check and lead a healthy lifestyle. If you want to learn more about these strategies, check out the next blog post, where we provide comprehensive information about diet, exercise, and medication to manage blood sugar effectively. Continue reading to receive practical tips that will help you to take control over your life!
Additional Considerations
This blog post has focused on the essential aspects of blood sugar and its management. However, it’s important to remember that blood sugar regulation can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Medications: Certain medications, including steroids and some antidepressants, can affect blood sugar levels.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and Cushing’s syndrome can also impact blood sugar control.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger the release of hormones that elevate blood sugar levels.
If you have any concerns or questions about your blood sugar or how various factors might influence it, consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended. They can provide personalised guidance based on your specific circumstances.
By understanding blood sugar, its role in your body, and the strategies to manage it, you can take charge of your health and live a vibrant, fulfilling life.